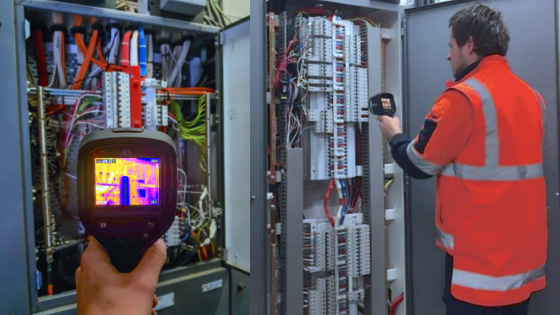
What thermal imaging is used for
Thermal imaging is used in a variety of applications, including security, search and rescue, building inspection, and scientific research.
Security: Thermal imaging can be used to detect people in low light or camouflaged conditions. It can also be used to monitor industrial processes for potential safety hazards.
Search and Rescue: Thermal imaging can be used to find people who are lost or stranded in dark or difficult to see environments. It can also be used to monitor large areas for signs of life.
Building Inspection: Thermal imaging can be used to detect leaks, moisture, and insulation problems in buildings. It can also be used to monitor the performance of solar panels and other energy-efficient devices.
Scientific Research: Thermal imaging can be used to study animal behavior, measure environmental conditions, and collect data for meteorological research.
How thermal imaging works
Thermal imaging cameras detect infrared radiation, which is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273°C). The amount of infrared radiation an object emits depends on its temperature.
The hotter an object is, the more infrared radiation it emits. Thermal imaging cameras convert the energy into an electrical signal, which is then displayed as an image. The image shows the relative temperatures of different objects in the scene.
The resolution of thermal images is determined by the number of pixels in the sensor array. More pixels means greater detail but also a larger file size. Thermal images are typically 8-bit or 16-bit grayscale images.
Thermal imaging cameras can be either handheld or mounted on a vehicle or drone. The camera’s field of view (FOV) is determined by the lens size. A larger lens will provide a wider FOV but will also be more expensive.
Thermal imaging cameras typically have a range of 1-14 µm. This means they can detect objects with temperatures between -273°C and +1,371°C.
Applications of thermal imaging
As mentioned before, thermal imaging has a variety of applications in both the public and private sector. Some of the most common applications are listed below:
Security: Thermal imaging can be used to detect people in low light or camouflaged conditions. It can also be used to monitor industrial processes for potential safety hazards.
Search and Rescue: Thermal imaging can be used to find people who are lost or stranded in dark or difficult to see environments. It can also be used to monitor large areas for signs of life.
Building Inspection: Thermal imaging can be used to detect leaks, moisture, and insulation problems in buildings. It can also be used to monitor the performance of solar panels and other energy-efficient devices.
Scientific Research: Thermal imaging can be used to study animal behavior, measure environmental conditions, and collect data for meteorological research.
The benefits of using thermal imaging
Thermal imaging has a number of advantages over other imaging technologies, such as visible light cameras. Some of the benefits of using thermal imaging are listed below:
1. Thermal imaging can be used in low light or dark conditions.
2. Thermal images are not affected by glare or reflection.
3. Thermal imaging can penetrate fog, smoke, and other obscurants.
4. Thermal images can be captured from a distance.
5. Thermal images can be stored and analyzed digitally.
6. Thermal imaging is non-invasive and does not emit any radiation.